We know about the conventional systems of electricity production, electricity transportation, and other things. Apart from the conventional methods, there are some other theoretical or experiment-based models where electricity is produced and carried, following different functions and laws. Microwave electricity is such an example where electricity is carried and transformed using a microwave frequency power harvesting system. Although the microwave does not act and travel as AC or DC current, this mechanism can absorb and convert the electromagnetic wave energy to DC voltage, the exact same energy unit that we use in our households.
Model Materials:
1)GIGAHERTZ MAGNETRON (Microwave source): When a circuit consists of a capacitor, voltage source, and an inductor, it is called an LC circuit. In this mechanism, a time-dependent function of the current caused by the acceleration of the electron is formed. This creates electromagnetic waves (microwave range).
2) RECTENNA (Antenna at the receiving end): Rectenna is a device that consists of antennas and rectifying diodes for a 2.45 GHz system. The antennas collect the microwave. When the microwave energy hits the rectifier, the electrons reach the conduction band and then create DC flow.
3) MICROWAVE TRANSMITTER
The electricity that is produced in the power plants is basically in the AC form. By using a Diode rectifier, AC electricity can be turned into DC electricity. DC electricity carries energy, which creates electromagnetic waves in microwave length. Microwave signals get to the destination where the wave’s energy will be converted to DC, which means electrical energy. Thus, we will have electricity to use.
Model Hypothesis:
1) Satellite electricity:
The energy of the power plant can be converted into microwaves and spread to the whole country. This may be possible, but the amount of energy loss is huge!
First of all, huge energy dissipation will occur for the microwave traveling to the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and ionosphere for collisions with air particles. Secondly, microwave – electricity and electricity – microwave conversion is responsible for a considerable amount of energy loss.So, we cannot compare electricity transmission with information transfer, because electricity transmission is related to energy efficiency.
2) Area by Area Model:
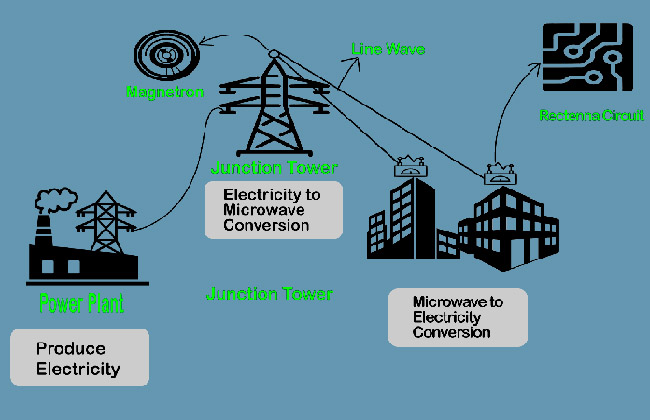
This model can reduce the excessive use of wires for transmission. From the power plants, the electricity will be transmitted to the junction, which is situated at a tall tower. From the tower, the electricity will be converted to microwaves by magnetron. Then the microwave will be transmitted to the top of the buildings as line signals (not as radiation that spreads). At the top of the buildings, there will be a receptor, which means rectenna, that will convert the microwave to DC, which will be used in households. This model does have some loss in energy dissipation by air molecules, in fact, a considerable amount of energy loss happens during the energy conversion in the magnetron and rectenna.
This model can be implemented like this – Dhaka is a city where wires are spread like spider waves, which creates a messy orientation. Assume that The Ashuganj power plant produces electricity for Dhaka. The electricity is transferred to Dhaka through the National Grid. There are 93 wards in Dhaka South City Corporation. The junction towers will be constructed for every 2-3 wards where electricity will be inter-transmitted without wire. The low-story houses, if get out of the electricity coverage, will get the connection from the adjacent taller building. This is a semi-wireless model, which will significantly reduce the use of excessive wires in Dhaka’s streets.
Why it is not in use:
First of all, when electricity gets converted into microwaves, and it travels a certain amount of path, the total amount of energy gets distorted and reduced. Another thing is that high-energy electromagnetic waves cause radiation that is very harmful toliving creatures, perhaps, creating a disturbance in radio communication systems. Machinery and instruments which are required for the conversion of energy sources are also pretty expensive and not reliable. Here it requires a direct line of sight which is not possible everywhere in the service area or may get interrupted frequently. Generally, n-p diodes are used in rectenna and there is a gap between the electron’s valence and conduction band. So, energy loss happens for the electrons gaining energy from the microwave to turn from the valence band to the conduction band. Gallium Arsenide rectenna can convert around a few GHz, in fact, if we use highly efficient optical rectenna, it needs difficult fabrication. Complexities and expenses have made it quite a fictional idea for urban implementation, restricting it to experiments only.
Abdullah Al Muhaimen is a student of Notre Dame College, Dhaka


